Describe the Three Primary Interventions for Hazard Control
Physical environmental and potential exposure. And help employers provide workers with safe and healthful working conditions.
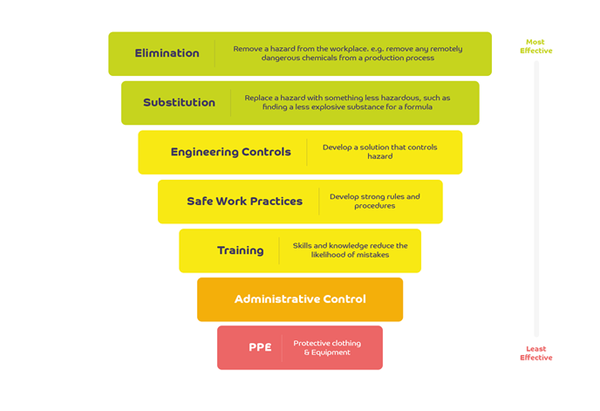
What Is The Hierarchy Of Control And How Can It Be Applied Bcarm
- Engineering controls which includes removal or redirection of the hazard such as with local and exhaust ventilation.
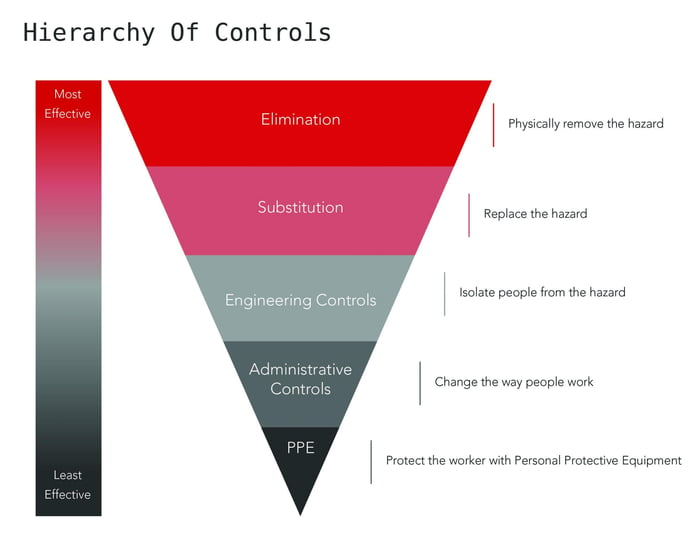
. Look at the physical work environment equipment materials products etc. Identifying Hazards Learning objectives in this module include. Effective controls protect workers from workplace hazards.
Help avoid injuries illnesses and incidents. Look at injury and incident records. Hazard Prevention and Control.
Describe the three primary interventions for hazard control. Risk avoidance involves an alternative strategy with a higher cost that would result in a higher probability of success. Outdoor work can also create hazards from vector- borne diseases from animals and insects and poisonous plants.
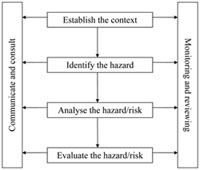
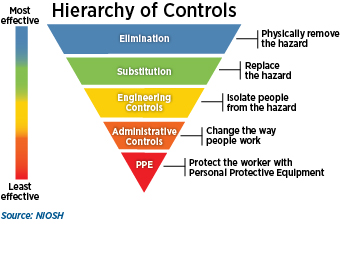
The hierarchy of control is a step-by-step approach to eliminating or reducing risks and it ranks risk controls from the highest level of protection and reliability through to the lowest and least reliable protection. Preservation of housekeeping and maintenance standards 6. Describe the three basic types of exposure to hazards.
Acceptance and use of personal protective equipment 5. General instruction and technical training. Hazard evaluation at the national state and local levels Implement hazard assessments as needed.
What are the three types of control methods for a hazard. Proper responses to emergency situations 8. A risk register outlines the risks associated with a particular project before and during the life of a project - and lists the accompanying details of those risks including how likely it is that that risk will occur and the impact ifwhen it does.
Engineering controls are the preferred method of eliminating or controlling hazards. Systems used to prevent and control hazards include. For example a common risk avoidance technique uses existing proven methodologies instead of adopting new.
4 proven methods for risk assessment. Minimize or eliminate safety and health risks. Eating well exercising regularly not smoking immunization against infectious diseases.
Local exhaust ventilation LEV to control risks from dust or fume is a common example as is separation of the hazard from operators by methods such as enclosing or guarding dangerous items of machineryequipment. Counseling family planning and the promotion of physical activity are other forms of health promotion. Look at all aspects of the work and include non-routine activities such as maintenance repair or cleaning.
Use of seatbelts and bike helmets education about healthy and safe habits eg. Legislation and enforcement to ban or control the use of hazardous products eg. Include how the tasks are done.
Increased awareness and recognition of workplace hazards 4. Childhood Experiences and toxic stress through primary secondary and tertiary prevention strategies. The company eliminates the safety issue by forcing employees to lower the light to the ground to work on it.
Eliminating the hazard and risk is the highest. Priority should be given to measures which protect collectively over individual measures. Environmental protection includes sanitation air quality control and food workplace and home safety.
In primary prevention health promotion includes education in many forms such as nutrition and sex education. Improvement of the public health system at the national state and local levels. Describe the two primary forms of safety education.
Discuss the importance of using checklists when conducting safety inspections. 1Engineering controls- elimination or minimizing of the hazard by designing facilities equipment to remove or process the hazardous materials or equipment. Define and give examples of hazards and exposures Describe the three basic types of OSHA-recognized hazards.
List and describe strategies to collect hazard control ideas. Describe the three primary interventions for hazard control. The hierarchy of control is a system for controlling risks in the workplace.
Examples include immunization and taking regular exercise. Proper use of hazard control systems in the workplace 2. Discuss the two ways to properly document safety instruction and technical training.
Talk to the workers. The main ways to control a hazard include. Remove the hazard from the workplace or substitute replace hazardous materials or machines with less hazardous ones.
Engineering Controls Administrative Controls Personal Protective Equipment PPE Systems to Track Hazard Correction Preventive Maintenance Systems Emergency Preparation Engineering Controls The first and best strategy is to control the hazard at its source. Adherence to accepted hygiene practices 7. Industry employer and common sense recognition.
- Administrative controls which includes written operating procedures work permits and safe work practices. Here are the 4 most common risk mitigation strategies. Respond to high-risk situations identify and quantify hazard-ous agents and facilitate exposure reduction.
Create a reliable and easily referenced risk register. Environmental hazards and health concerns. The processes described in this section will help employers prevent and control hazards identified in the previous section.
Engineering control hazards at the source. Secondary prevention those preventive measures that lead to early diagnosis and prompt treatment of a disease illness or injury to prevent more severe problems developing. The hazard control hierarchy contains the five following levels starting with the most effective and going to the least effective.
Elimination Substitution Redesign Isolation Automation List 5 types of engineering controls. They know their job and its hazards best. John and Morris run the risk of falling while repairing an overhead light.
Includes designs or modifications to plants equipment ventilation systems and processes that reduce the source of exposure. Engineering controls consist of a variety of methods for minimizing hazards including process control enclosure and isolation and ventilation. The 5 types of engineering controls are.
Development of safe work habits 3. Asbestos or to mandate safe and healthy practices eg. Primary preventionthose preventive measures that prevent the onset of illness or injury before the disease process begins.
Process controls involve changing the way that a job activity is performed in order to reduce risk. For example public health surveillance ie tracking health and disease patterns over time and epidemiologic study ie investigating risk and protective factors and evaluating effectiveness of interventions provide critical.

Hierarchy Of Control Workplace Health And Safety Conserve

Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty Versus 0 5 Timolol Eye Drops For The Treatment Of Glaucoma In Tanzania A Randomised Controlled Trial The Lancet Global Health

How To Control Chemical Hazards In The Workplace
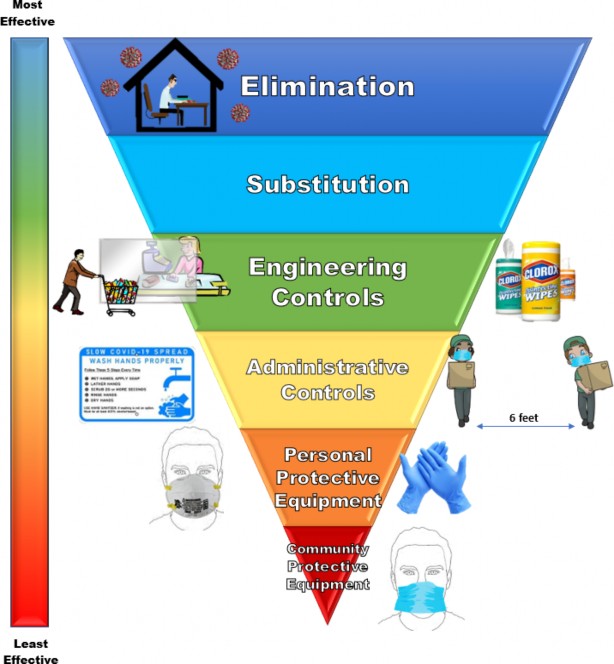
Covid 19 Hierarchy Of Controls Environment Health And Safety

Protocol Safety Interventions For The Prevention Of Accidents At Work Dyreborg 2015 Campbell Systematic Reviews Wiley Online Library
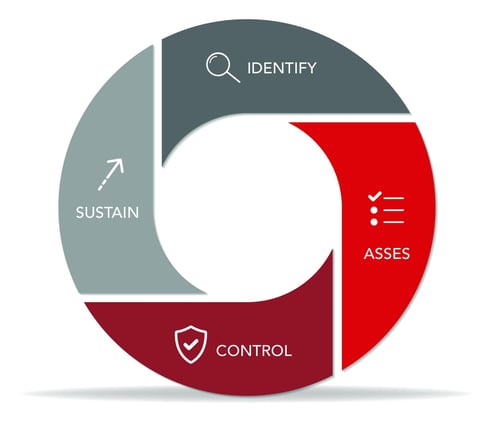
How To Control Chemical Hazards In The Workplace
Hygiene And Environmental Health Module 2 Environmental Health Hazards View As Single Page
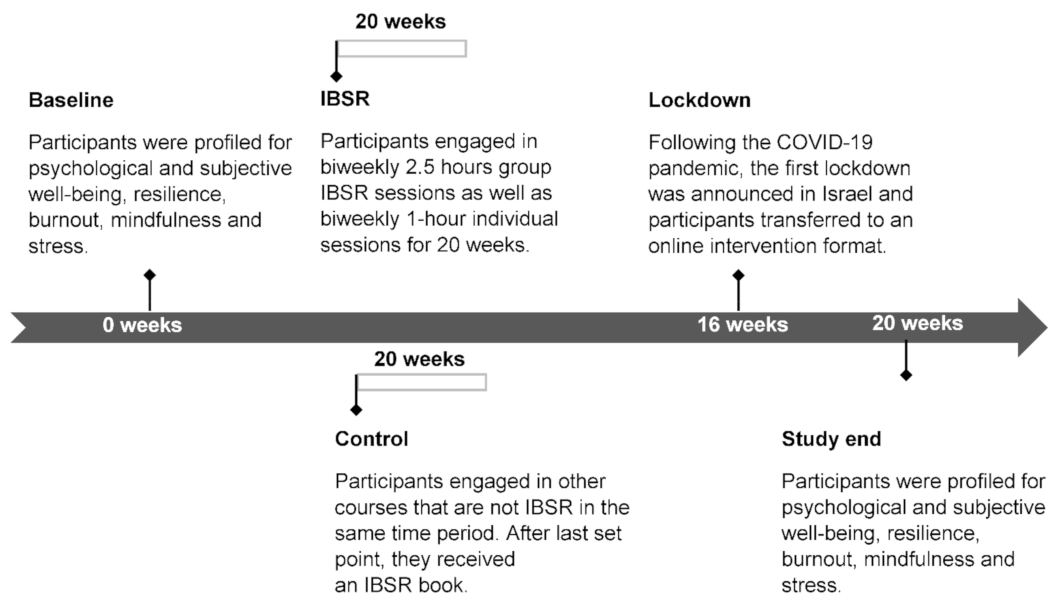
Ijerph Free Full Text Effect Of Inquiry Based Stress Reduction Ibsr Intervention On Well Being Resilience And Burnout Of Teachers During The Covid 19 Pandemic Html
Methods For Controlling Hazards Ufcw Safety And Health Website

Infection Prevention And Control 3 Risk Management In Ipc
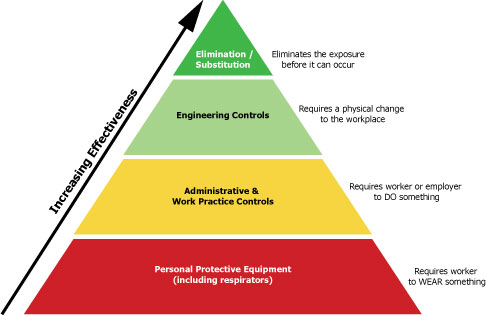
Chemical Hazards And Toxic Substances Controlling Exposure Occupational Safety And Health Administration

Risk Management An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Infection Prevention And Control 3 Risk Management In Ipc
Chemical And Biological Hazard Prevention
Safety Management Hazard Prevention And Control Occupational Safety And Health Administration

How Can Occupational Safety And Health Be Managed Labour Administration And Inspection

Protocol Safety Interventions For The Prevention Of Accidents At Work Dyreborg 2015 Campbell Systematic Reviews Wiley Online Library


Comments
Post a Comment